ZITADEL with Go
This integration guide shows you how to integrate ZITADEL into your Go API. It demonstrates how to secure your API using OAuth 2 Token Introspection.
At the end of the guide you should have an API with a protected endpoint.
This documentation references our HTTP example. There's also one for GRPC. Check them out on GitHub.
Set up application and obtain keys
Before we begin developing our API, we need to perform a few configuration steps in the ZITADEL Console. You'll need to provide some information about your app. We recommend creating a new app to start from scratch. Navigate to your Project, then add a new application at the top of the page. Select the API application type and continue.
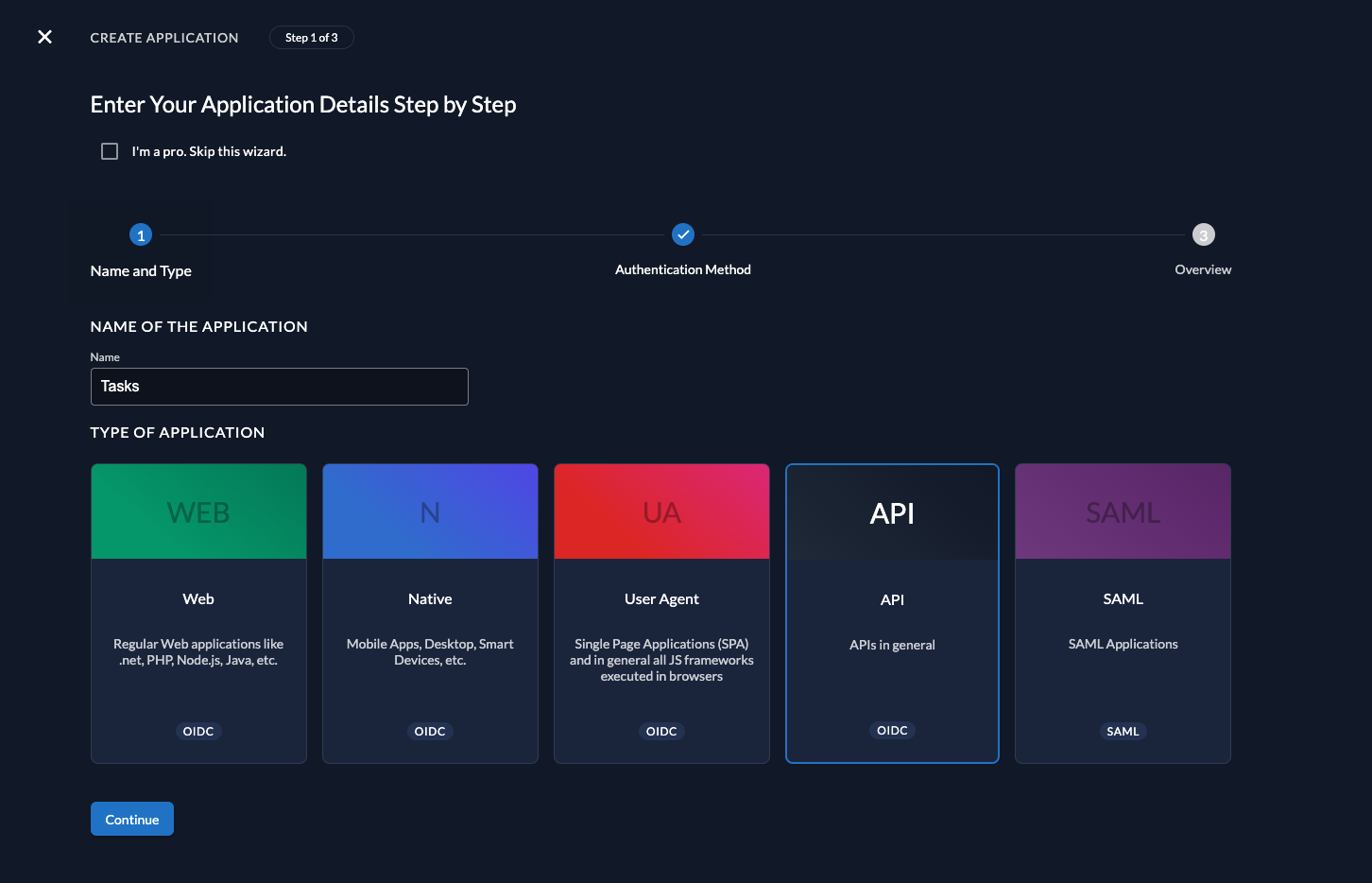
We recommend that you use JWT Profile for authenticating at the Introspection Endpoint.
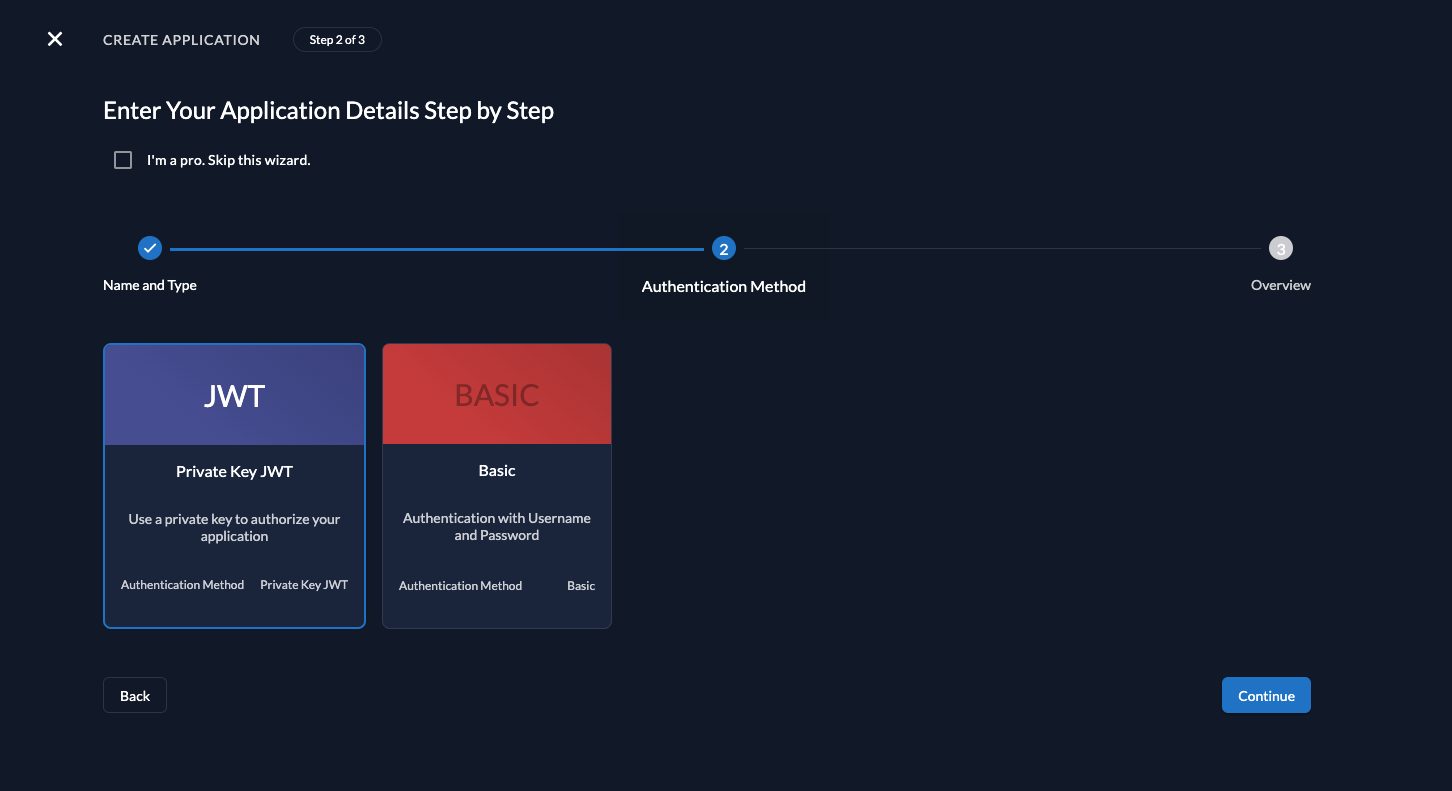
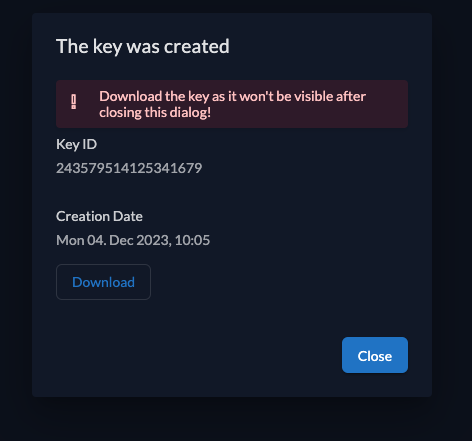
Then create a new key with your desired expiration date. Be sure to download it, as you won't be able to retrieve it again.
Prerequisites
This will handle the OAuth 2.0 introspection request including authentication using JWT with Private Key using our OIDC client library.
All that is required, is to create your API and download the private key file later called Key JSON for the service user.
Go Setup
Add Go SDK to your project
You need to add the SDK into Go Modules by:
go get -u github.com/zitadel/zitadel-go/v3
Create example API
Create a new go file with the content below. This will create an API with three endpoints:
/api/healthz: can be called by anyone and always returnsOK/api/tasks: requires authorization and returns the available tasks/api/add-task: requires authorization with grantedadminrole and adds the task to the list
If authorization is required, the token must not be expired and the API has to be part of the audience (either client_id or project_id).
For tests we will use a Personal Access Token.
https://github.com/zitadel/zitadel-go/blob/next/example/api/http/main.go
You will need to provide some values for the program to run:
domain: Your ZITADEL instance domain, e.g. https://my-domain.zitadel.cloudkey: The path to the downloaded key.jsonport: The port on which the API will be accessible, default it 8089
Test API
After you have configured everything correctly, you can simply start the example by:
go run main.go --domain <your domain> --key <path>
This could look like:
go run main.go --domain my-domain.zitadel.cloud --key ./api.json
After you get a successful log:
2023/12/04 10:27:42 INFO server listening, press ctrl+c to stop addr=http://localhost:8089
Public endpoint
Now you can call the API by browser or curl. Try the healthz endpoint first:
curl -i http://localhost:8089/api/healthz
it should return something like:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Mon, 04 Dec 2023 09:29:38 GMT
Content-Length: 4
"OK"
Task list
and the task list endpoint:
curl -i http://localhost:8089/api/tasks
it will return:
HTTP/1.1 401 Unauthorized
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
Date: Mon, 04 Dec 2023 09:41:54 GMT
Content-Length: 44
unauthorized: authorization header is empty
Get a valid access_token for the API. You can either achieve this by getting an access token with the project_id in the audience or use a PAT of a service account.
If you provide a valid Bearer Token:
curl -i -H "Authorization: Bearer ${token}" http://localhost:8089/api/tasks
it will return an empty list:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Mon, 04 Dec 2023 09:49:06 GMT
Content-Length: 2
{}
Try to add a new task
Let's see what happens if you call the AddTask endpoint:
curl -i -H "Authorization: Bearer ${token}" http://localhost:8089/api/add-task
it will complain about the missing admin role:
HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden
Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
Date: Mon, 04 Dec 2023 09:52:00 GMT
Content-Length: 50
permission denied: missing required role: `admin`
Add admin role
So let's create the role and grant it to the user. To do so, go to your project in ZITADEL Console
and create the role by selecting Roles in the navigation and then clicking on the New Role button.
Finally, create the role as shown below:
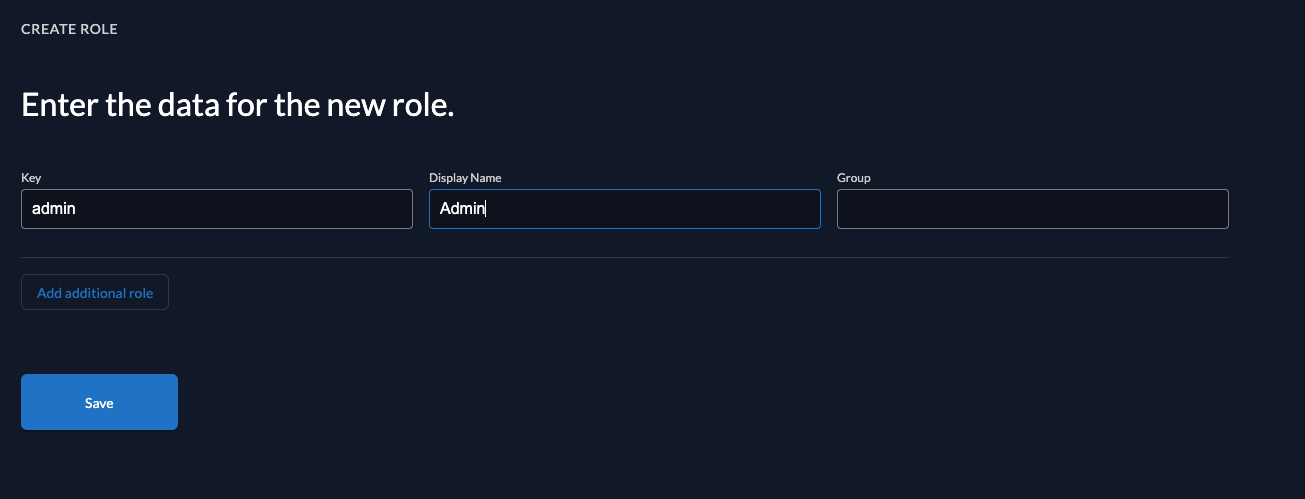
After you have created the role, let's grant it the user, who requested the tasks.
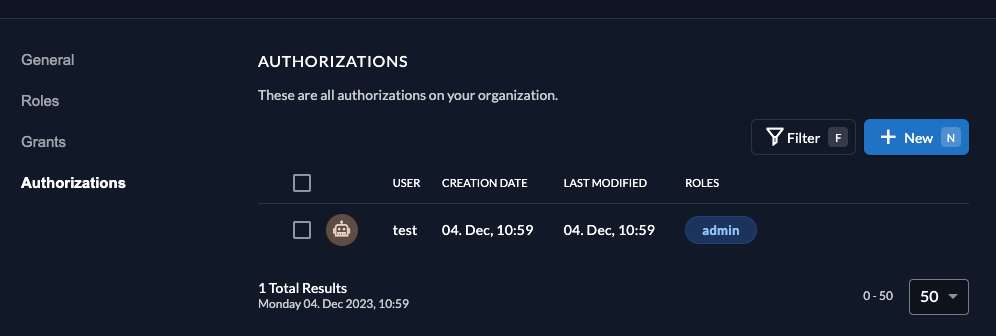
Click on Authorization in the navigation and create a new one by selecting the user and the admin role.
After successful creation, it should look like:
So you should now be able to add a new task:
curl -i -H "Authorization: Bearer ${token}" http://localhost:8089/api/add-task --data "task=My new task"
which will report back the successful addition:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Mon, 04 Dec 2023 10:06:29 GMT
Content-Length: 26
"task `My new task` added"
Let's now retrieve the task list again:
curl -i -H "Authorization: Bearer ${token}" http://localhost:8089/api/tasks
As you can see your new task ist listed. And since you're an admin now, you will always get an additional create a new task on /api/add-task:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Date: Mon, 04 Dec 2023 10:08:38 GMT
Content-Length: 62
{"tasks":["My new task","create a new task on /api/add-task"]}